valgus force & active radiocapitellar compression test|valgus force vs varus : distribution Valgus alignment is known as knock knee syndrome. It shifts the load-bearing axis to the outside of the knee joint, forcing the knees to be positioned inward. Varus alignment, or bow leg syndrome, causes the load . 1 95,4K. brasiloirinha-jefao Lindogato. 13 115,1K. Thay Napoleão (Brasiloirinha) PACKSBRVIPOFICIAL. 4 4 143,7K. VAZOU BRASILOIRINHA VÍDEOS NOVOS 2024 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web24 de jan. de 2024 · Da redação Diego Alves No início da noite desta última segunda-feira (22), durante um patrulhamento de Força Tática no bairro Jardim do Lago, em .
The valgus stress test, also known as the medial stress test, is used to assess the integrity of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) of the knee. MCL injuries are common in the athletic population and can occur as either isolated injuries, or combined with other structural injuries . See moreOverall, the MCL plays a crucial role in the stability of the knee and acts as the primary valgus restraint in a flexed knee. If knee hypermobility is present due to a sprained MCL, the ACL is placed under higher stress loads with valgus forces (particularly at 45 . See more “Valgus” is the medical term for a force that pushes in toward the center of your body. Your provider will press your knee or elbow in, toward your body during a valgus stress . Valgus alignment is known as knock knee syndrome. It shifts the load-bearing axis to the outside of the knee joint, forcing the knees to be positioned inward. Varus alignment, or bow leg syndrome, causes the load .
A medial collateral ligament (MCL) knee injury is a traumatic knee injury that typically occurs as a result of a sudden valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected with increased valgus laxity .The valgus stress test or medial stress test is a test for damage to the medial collateral ligament of the knee. It involves placing the leg into extension, with one hand placed as a pivot on the .
There are two collateral ligaments of the knee: the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Injuries of the MCL are much more common, owing to its exposure .A medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury is a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. It is one of the most common knee injuries and results mostly from a valgus force on the knee [1] [2].A valgus force is one that pushes the outside of the knee inwards, causing a stretching of the medial structures. Generally, this occurs from impact, or when the lower leg is in contact .Inward (valgus) force: Usually, the medial collateral ligament, followed by the anterior cruciate ligament, then the medial meniscus (this mechanism is the most common and is usually accompanied by some external rotation and flexion, as .
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia. Its role is to provide .While palpating the medial joint line, the examiner should apply a valgus force to the patient's knee. A positive test occurs when pain or excessive gapping occurs (some gapping is normal at 30 degrees). Be sure to not include rotation of the .A valgus force and axial load are applied to the knee at the same time. Upon damage to the ACL, there will be subluxation of the lateral tibial plateau in the fully extended position. When the knee is flexed between 20 o and 40 o , the lateral tibial plateau will reduce itself, and a palpable shift or clunk will be noticed. The medial collateral ligament, anterior capsule, and articulation provide 54%, 10%, and 36%, respectively, for resisting the valgus force in the 90° flexion of elbow joint . The anterior bundle of medial collateral ligament is the primary stabilizer and the radial head is a secondary stabilizer of the elbow to resist the valgus force .
Dynamic valgus is a thing, but it isn’t the boogeyman many make it out to be; To sustain a non-contact ACL tear you need dynamic valgus, but you need other things as well; Dynamic valgus adds load to the patellofemoral joint, but the joint can become conditioned to tolerate it; Variation of movement is a beautiful and wonderful thing
what direction is valgus force
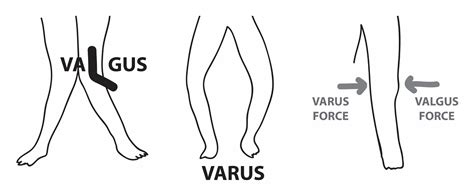
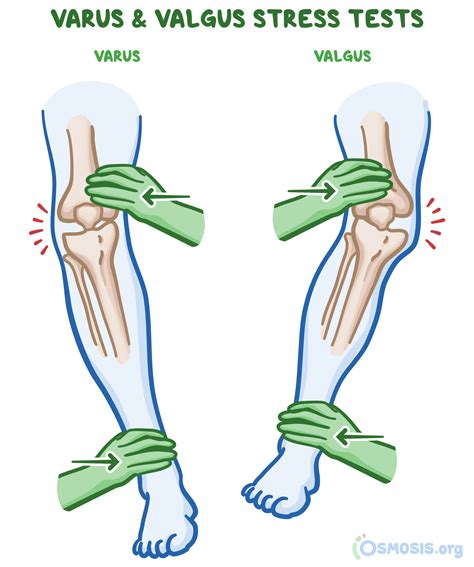
valgus vs varus stress
A valgus deformity is a condition in which the bone segment distal to a joint is angled outward, that is, angled laterally, away from the body's midline. [1] The opposite deformation, where the twist or angulation is directed medially, toward the center of the body, is called varus .Definition/Description [edit | edit source]. A medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury is a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. It is one of the most common knee injuries and results mostly from a valgus force on the knee .. Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]
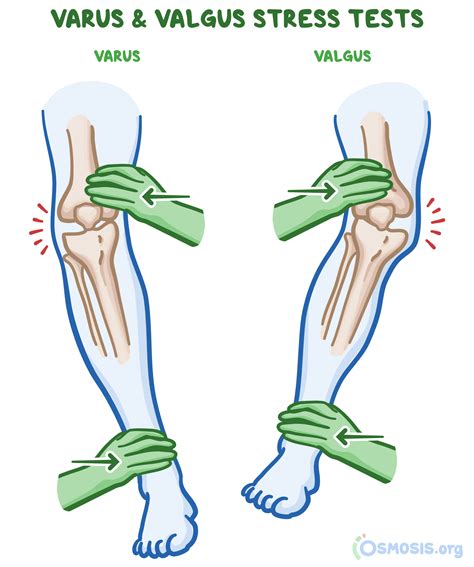
The valgus force routinely applied by clinicians is unknown, but it is certain to vary. For the purpose of this study, we initially monitored the real-time applied force on the computer screen up to 120 N, but for statistical analysis, data were retrieved for only 60 N. Trials were repeated, typically 3 to 5 times, until 2 trials of slope .
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) consists of three bundles - the anterior oblique ligament/bundle (AOL), the posterior oblique ligament/bundle (POL) and the transverse ligament (which unites AOL and POL)[1][2]. Of the three bundles, the AOL is the strongest and provides significant restraint to valgus force when the elbow is between 30 and 120 degrees flexion.Approximately 20° of internal rotation is applied to the tibia and the knee is placed in full extension. A valgus force is applied to the knee as it is slowly flexed. An anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knee will remain reduced in full extension but will sublux around 20–30° of knee flexion and then will reduce again in deeper flexion.The test should also be performed with the knee positioned into 30 degrees of flexion, applying the same valgus force at the knee. How to Interpret Valgus Stress Test. Positive Finding: A positive test occurs when gapping or pain is noted with this test in full knee extension; this may suggest both an MCL and cruciate injury. With the knee at .
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.MCL injury. Patients commonly have had recent excessive valgus force applied to a partially flexed knee (eg, a clipping injury in football). A common triad of injury (particularly in athletes) when a valgus force is applied to the knee involves injury to the MCL, the medial meniscus, and the anterior cruciate ligament. the radial head provides approximately 30% of valgus stability. this is most important at 0-30 deg of flexion/pronation. capsule. . Joint reaction force. there are large joint reaction forces due to short and inefficient lever arms around elbow (biceps inserts not far from center of rotation)
A valgus force is applied by pulling the patient’s thumb while the examiner’s other hand stabilizes the elbow and palpates the medial joint line. A modification of the milking maneuver is performed with the shoulder adducted, maximally externally rotated, and the elbow flexed to 70° as a valgus stress is applied by pulling the thumb. 9A combination of valgus and external rotation force has been proposed. 2,9,18,22,35 Associated injuries after trauma may include fractures of the radial head, olecranon, or medial humeral epicondyle. 22,35 Medial collateral . The terms valgus and varus refer to angulation (or bowing) within the shaft of a bone or at a joint in the coronal plane. It is determined by the distal part being more medial or lateral than it should be. Whenever the distal part is more lateral, it is called valgus. Whenever the distal part is more medial, it is called varus.
In the current study, the authors aimed to determine the minimum amount of valgus force required to elicit a positive pivot shift test utilizing a mechanized pivot shifter device in ACL-deficient knees. The authors proposed that increasing the applied force from a minimum critical value would lead to greater magnitudes of femoro-tibial translation. A direct valgus force is applied against the post for viewing the medial compartment. A varus force is applied by dropping the post and placing the leg in a figure-of-4 position. The arrow marks the button that is pressed to lower the post. After the tourniquet is placed, the circumferential leg holder (Smith & Nephew, Andover, MA) or lateral . The valgus moment of force on the right lower limb was calculated using the technique by Hamill and Selbie . The proximal local coordinate system of the knee was oriented so that the valgus moment in the frontal plane of the thigh provided positive numbers and initiated a tendency towards adduction (the movement of the calf toward the middle . What is Valgus Stress? Valgus stress refers to a specific type of force applied to a joint that causes the limb to bend outward, placing strain on the inner part of the structure. This term is most commonly associated with the knee, where it reflects the lateral force pushing the lower leg away from the upper leg.
The therapist then applies a valgus force to the elbow. If the patient experiences pain or excessive gapping compared to the contralateral side the test is considered positive. Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown. Importance of Test: The MCL of the elbow is a common injury among overhead throwers. According to Neumann, the MCL of the elbow has 3 fiber .
This is likely due to the increased hip adduction motion that results in dynamic valgus at the knee which predisposes the ACL to higher levels of shear force [15,18,52]. Despite the controversy on peak hip flexion, it is apparent that movement and strength at the hip contributes to ACL risk susceptibility. ⚡ Welcome to Catalyst University! I am Kevin Tokoph, PT, DPT. I hope you enjoy the video! Please leave a like and subscribe! 🙏INSTAGRAM | @thecatalystuniver. In soccer, where there is a high incidence of MCL injuries, there are three mechanisms for injury: direct contact to the knee with a valgus force, contact to the leg or foot creating a valgus force on the knee, or slide tackling that creates a valgus force . MCL tears can occur in isolation or as part of a multi-ligamentous injury.A force was manually applied to the end-point of varus and valgus knee laxity and the measured change in mechanical alignment was recorded. Force was applied with the knee positioned in increments of flexion from 0 to 90°. In keeping with previous studies, satisfactory values of coefficient of repeatability (CR) of 1.55 and 1.33 were found for .
Place your hip against the lateral knee and use it as a fulcrum to apply a valgus force at the knee (distal hand at the foot/ankle). Compare to the opposite, unaffected side. Seated testing. Flex the involved knee to 30° Support the medial ankle with one hand; Apply a valgus force (lateral to medial) at the knee – check for painFlexor pronator muscles (FPMs) play a key role in stabilizing the elbow joint against valgus forces. However, no studies have investigated the in vivo kinematics of FPMs against these forces on the elbow. This study aimed to clarify the in vivo contribution of each FPM as a dynamic stabilizer in a c .
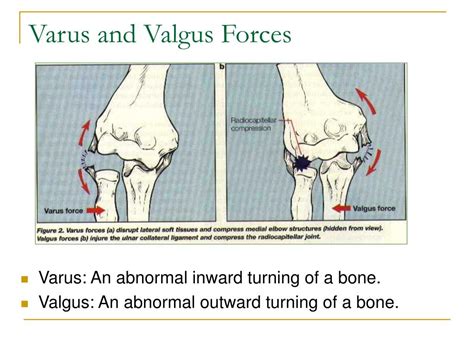
valgus vs varus force elbow
dynamic hardness tester manual
Sara estanislau | Lua santana. 81 members. @brasiloirinha. Open a Channel via Telegram app. Preview channel. Don't have Telegram yet? Open via web telegram.
valgus force & active radiocapitellar compression test|valgus force vs varus